On April 10, 2025, the 13th Energy Storage International Conference and Expo (ESIE 2025), jointly hosted by the China Energy Research Society, the China Energy Storage Alliance (CNESA), and the Institute of Engineering Thermophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, was grandly held at the Beijing Capital International Convention and Exhibition Center. Concurrently, the 2024 Rankings of Chinese Energy Storage Companies were officially released. Over 40 companies made the list, with CATL, Shoto, Kehua Tech, Sungrow, CRRC Zhuzhou Institute, and JD Energy topping the respective rankings.
About the CNESA Annual Energy Storage Company Rankings
Since 2015, the China Energy Storage Alliance has been publishing the “Annual Energy Storage Company Rankings.” Over the past 10 years, these rankings have received broad attention and high recognition from industry peers. CNESA objectively presents the competitive landscape of Chinese companies in both domestic and global markets through shipment data of energy storage products and project installation data. The changes in the rankings over the years not only reflect the industry’s level of concentration but also mirror the global competitiveness of Chinese enterprises.
The shipment data and project installation data of the companies on the list are all sourced from the CNESA DataLink Global Energy Storage Database (https://www.esresearch.com.cn). Independently developed by CNESA since 2011, the database is the world's first full-chain, one-stop, intelligent data service platform. It includes project library, policy library, manufacturer library, product library, bidding library, investment and financing library, standards library, and research report library. Today, the database is frequently cited by international organizations, governments, official and social media, securities firms, and energy storage companies. Its objectivity and authority have been widely recognized within the industry. In 2022, it won the second prize of the China Energy Research Society Energy Innovation Award and obtained software copyright registration in the same year.
To ensure the quality and comprehensiveness of energy storage data statistics, and to objectively analyze the development status of the energy storage industry for the year and forecast future trends, CNESA regularly collects and compiles data from the global energy storage market through multiple channels. Through multi-dimensional data verification and on an annual basis, it conducts statistical analysis on the installation and shipment data of energy storage products (excluding OEM/contract manufacturing) from Chinese energy storage technology providers, PCS providers, and system integrators in both domestic and global markets.
2024 Rankings of Chinese Energy Storage Companies
Ranking of Chinese Energy Storage Technology Providers:
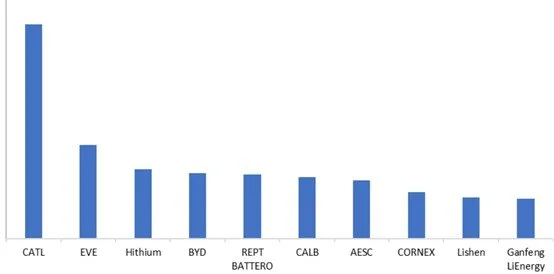
In 2024, in the global market, the top ten Chinese companies by shipment volume of energy storage batteries (excluding backup power batteries for base stations/data centers) were: CATL, EVE, Hithium, BYD, REPT BATTERO, CALB, AESC, CORNEX, Lishen, and Ganfeng LiEnergy.
Figure 1: Top 10 Chinese energy storage technology providers in the 2024 global market, Unit: GWh
Notes:
CNESA defines energy storage technology providers as companies with the capability to manufacture core energy storage technologies and supply core energy storage technology products to customers. The core technology includes energy storage cells, physical storage, etc.
The statistical scope refers to the global shipment volume in 2024 of energy storage cells independently produced by enterprises (excluding base station and data center cells). Shipment volume refers to cells that have been manufactured and delivered to customers or project sites.
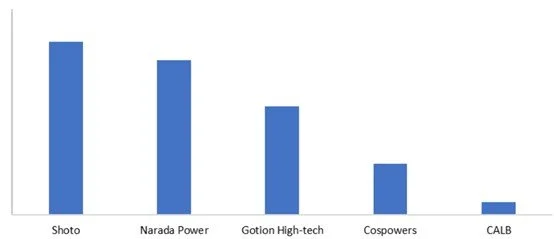
In 2024, in the global market, the top five Chinese companies by shipment volume of backup power batteries for base stations/data centers were: Shoto, Narada Power, Gotion High-Tech, Cospowers, and CALB.
Figure 2: Top 5 Chinese energy storage base station/IDC technology providers in the 2024 global market, Unit: GWh
Note: The shipment data of backup power batteries for base stations/data centers includes both lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries.
Ranking of Chinese Energy Storage PCS Providers:
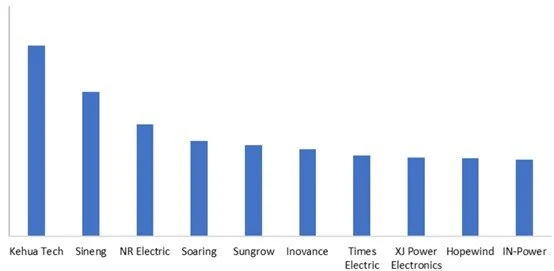
In 2024, in the domestic market, the top ten Chinese companies by shipment volume of energy storage PCS were: Kehua Tech, Sineng, NA Electric, Soaring, Sungrow, Inovance, Times Electric, XJ Power Electronics, Hopewind, and IN-Power.
Figure 3: Top 10 Chinese energy storage PCS providers ranked by number of shipments in the 2024 domestic market, Unit: GW
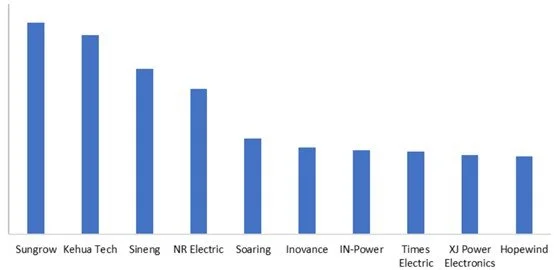
In 2024, in the global market, the top ten Chinese companies by shipment volume of energy storage PCS were: Sungrow, Kehua Tech, Sineng, NR Electric, Soaring, Inovance, IN-Power, Times Electric, XJ Power Electronics, and Hopewind.
Figure 4: Top 10 Chinese energy storage PCS providers ranked by number of shipments in the 2024 global market, Unit: GW
Ranking of Chinese Energy Storage System Integrators:
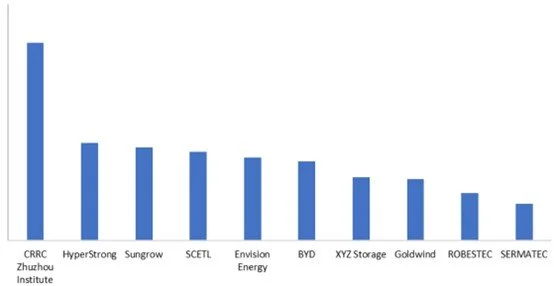
In 2024, in the domestic market, the top ten Chinese companies by installed capacity of grid-connected energy storage systems were: CRRC Zhuzhou Institute, HyperStrong, Sungrow, SCETL, Envision Energy, BYD, XYZ Storage, Goldwind, ROBESTEC, and SERMATEC.
Figure 5: Top 10 Chinese ESS integrators ranked by number of commissioned ESS installations in the 2024 domestic market, Unit: GWh
Note: Energy storage systems specifically refer to AC-side systems composed of energy storage battery DC systems, PCS and boost systems, EMS, and other related auxiliary equipment. Same applies below.
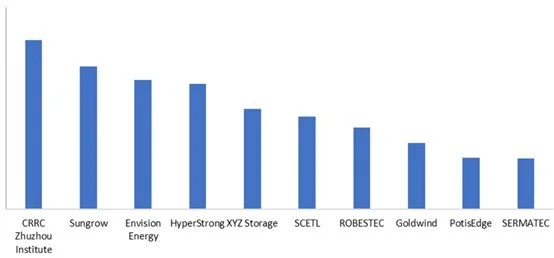
In 2024, in the domestic market, the top ten Chinese companies by shipment volume of energy storage systems were: CRRC Zhuzhou Institute, Sungrow, Envision Energy, HyperStrong, XYZ Storage, SCETL, ROBESTEC, Goldwind, PotisEdge, and SERMATEC.
Figure 6: Top 10 Chinese EES integrators ranked by number of shipments in the 2024 domestic market, Unit: GWh
In 2024, in the global market, the top ten Chinese companies by shipment volume of energy storage systems were: Sungrow, CRRC Zhuzhou Institute, Envision Energy, HyperStrong, XYZ Storage, SCETL, ROBESTEC, Goldwind, Trina Storage, and Sunwoda Energy.
Figure 7: Top 10 Chinese EES integrators ranked by number of shipments in the 2024 global market, Unit: GWh
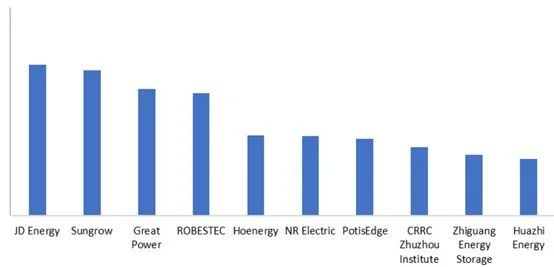
In 2024, in the domestic behind-the-meter (user-side) market, the top ten Chinese companies by shipment volume of energy storage systems were: JD Energy, Sungrow, Great Power, ROBESTEC, Hoenergy, NR Electric, PotisEdge, CRRC Zhuzhou Institute, Zhiguang Energy Storage, and Huazhi Energy.
Figure 8: Top 10 Chinese EES integrators ranked by number of shipments in the 2023 domestic user-side market, Unit: MWh