On May 20, the China Energy Storage Alliance hosted the “Assessing Energy Storage’s Development Trends and the Energy Storage Industry White Paper 2020” webinar, which featured support from Sungrow, CLOU, Higee, and Hyperstrong. During the webinar, CNESA Vice General Secretary and Research Director Yue Fen announced the official launch of CNESA’s Energy Storage Industry White Paper 2020.
This year marks the 10-year anniversary of the CNESA Energy Storage Industry White Paper. Over these past 10 years, the CNESA white paper has closely followed the development of China’s energy storage market, earning broad recognition and praise within the industry. The Energy Storage Industry White Paper 2020 provides summary and analysis of the 2019 energy storage market size, policies, projects, vendors, and standards from both the global and Chinese market perspectives, and provides predictions and outlook on future market development both in China and worldwide.
The webinar began with an opening address from China Energy Storage Alliance Chairman Chen Haisheng, followed by presentations on the development and outlook of energy storage from China State Grid Dispatch Center Professor-level Engineer Pei Zheyi and China Energy Research Society Renewable Energy Committee Director Li Junfeng. In discussing the growth of energy storage over the past ten years, CNESA Secretary General Liu Wei expressed warmly, “ten years of the Energy Storage Industry White Paper represents ten years of industry development, and ten years of CNESA growth from ‘zero to one.’” Over these past ten years, CNESA has earned support, care, and direction from many leading industry experts and companies. Over the next ten years, CNESA will continue to work together with our industry colleagues to support the continued growth of the energy storage industry.
1. Global Energy Storage Market Growth in 2019
According to statistics from the CNESA Global Energy Storage Projects Database, by the end of 2019, global operational energy storage project capacity totaled 184.6GW, an increase of 1.9% compared to the previous year. Pumped hydro energy storage comprised the largest portion of global capacity at 171.0 GW, a growth of 0.2% compared with 2018. Electrochemical energy storage followed with a total capacity of 9520.5MW. Among the variety of electrochemical energy storage technologies, lithium-ion batteries made up the largest portion of the capacity, at 8453.9MW.
Figure 1: accumulated global energy storage market capacity (2000-2019)
Figure 2: accumulated global electrochemical energy storage market capacity (2000-2019)
In 2019, new operational electrochemical energy storage projects were primarily distributed throughout 49 countries and regions. By scale of newly installed capacity, the top 10 countries were China, the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, Australia, Japan, the United Arab Emirates, Canada, Italy, and Jordan, accounting for 91.6% of the globe’s new energy storage capacity in 2019.
In comparison to the 2018 rankings, China, the United States, Germany, Japan, and Canada each moved up one to two places respectively in ranking, with China jumping from second place in 2018 to first in 2019. Both the United Kingdom and Australia occupied the third and fifth spots in 2018 and 2019, respectively, while the United Arab Emirates, Italy, and Jordan were new entrants to the list. In terms of geographic distribution, the countries on the list are mainly located in the Asia-Pacific (3), Europe (3), North America (2) and the Middle East (2). In terms of installed capacity, the top seven countries all added over 100 megawatts of new project capacity, with new capacity in China and the United States each both exceeding 500MW.
2. Chinese Energy Storage Market Growth in 2019
According to statistics from the CNESA Global Energy Storage Project Database, by the end of 2019, operational energy storage project capacity in China totaled 32.4GW, accounting for 17.6% of total global capacity, a growth of 3.6% compared to 2018. Pumped hydro projects accounted for the largest portion of installed capacity, at 30.3GW, an increase of 1.0% compared with 2018. Electrochemical energy storage capacity ranked second, at 1709.6MW, a growth of 59.4% compared to 2018. Among the variety of electrochemical energy storage technologies, lithium-ion batteries made up the largest portion of installed capacity at 1378.3MW.
In recent years, electrochemical energy storage has maintained a steady upward trend, with a compound annual growth rate of 79.7% from 2015-2019. In contrast, physical energy storage growth has been much slower, though technologies such as compressed air energy storage and flywheels saw new application breakthroughs in 2019. More than 2.2GW of new CAES project capacity was announced or began construction in 2019, including the start of construction on the Gezhouba Shandong Feicheng 1.25GW/7.5GWh salt cave CAES project, the nation’s first GW-scale CAES energy storage project. New breakthroughs in flywheel technologies included the deployment of the Beijing Metro Guanyangcheng Station GTR 1MW flywheel system, a MW-level flywheel application and the first in the country to provide a solution for regenerative braking energy recovery in urban rail transit.
Figure 3:accumulated energy storage capacity in China (2000-2019)
Figure 4:accumulated electrochemical energy storage capacity in China (2000-2019)
In 2019, China’s new operational electrochemical energy storage capacity was distributed primarily in 28 provinces and cities (including Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan regions). The ten regions with the largest increases in new capacity were Guangdong, Jiangsu, Hunan, Xinjiang, Qinghai, Beijing, Anhui, Shanxi, Zhejiang, and Henan. New energy storage capacity in these regions accounted for 88.9% of China’s total new capacity in 2019.
3. Chinese Energy Storage Market Development Outlook
Since 2014, the CNESA research department has been forecasting the scale of China's energy storage market with the support of industry experts and energy storage companies. The Energy Storage Industry White Paper 2020 provides a forecast for the scale and development trends of China's energy storage market from 2020-2024.
To provide a more comprehensive understanding of the future development of electrochemical energy storage, the CNESA research department has divided its 2020-2024 forecast into a conservative scenario and ideal scenario. These predictions are as follows:
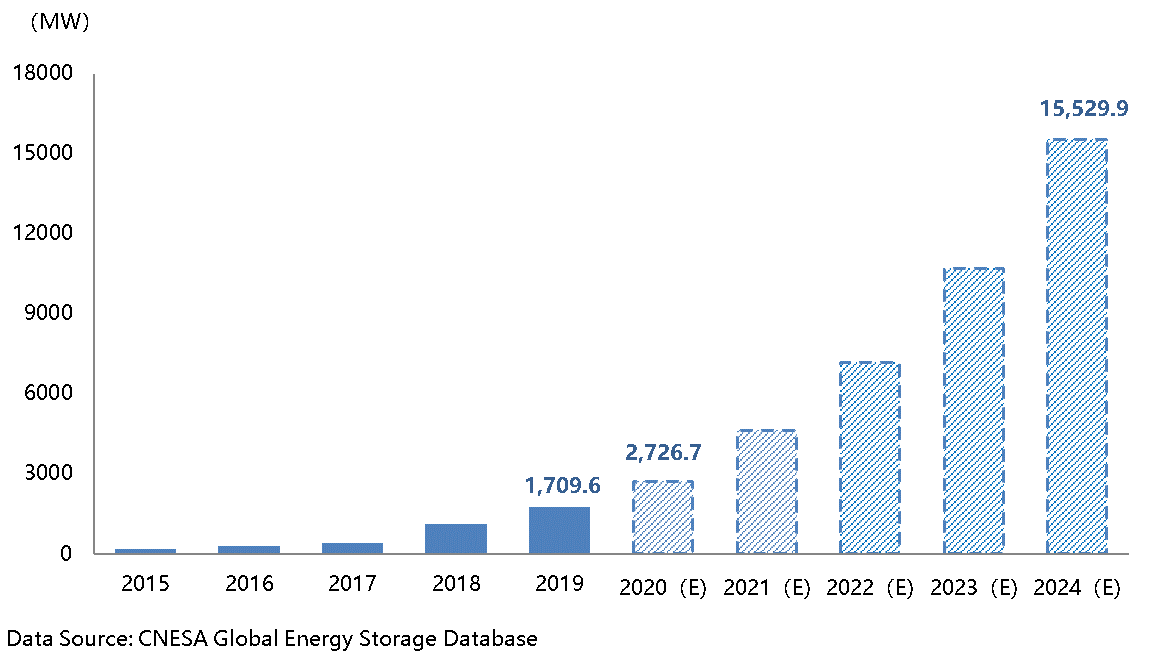
Conservative Scenario: In 2020, the electrochemical energy storage market will continue to develop steadily, and the total operational installed capacity will reach 2726.7MW. During the "14th Five-year Plan" period, as more favorable policies are issued, support for electrochemical energy storage applications will gradually increase and the market scale will continue to expand. The annual compound growth rate (2020-2024) will remain around 55%. By the end of 2024, the market scale of operational electrochemical energy storage is expected to exceed 15GW.
Figure 5:forecast for growth in total operational electrochemical energy storage capacity in China (conservative scenario, 2020-2024)
Ideal Scenario: In 2020, as electrochemical energy storage continues to develop steadily, some pipeline projects that were planned for 2019 but not constructed due to policy influences will be restarted. Thus, the total operational capacity will reach 3092.2MW. During the "14th Five-year Plan" period, taking into account the support of various direct and indirect policies, the annual compound growth rate for 2020-2024 is expected to exceed 65%. By the end of 2024, the total installed scale of electrochemical energy storage is expected to be near to 24GW.
Figure 6:forecast for growth in total operational electrochemical energy storage capacity in China (ideal scenario, 2020-2024)
Whether it is the conservative or the ideal scenario which will play out, the rapid development of the energy storage industry is irreversible. The early growth of energy storage technology and industry has laid a solid foundation for vitality and sustainable development. The development demands of the energy revolution, especially the large-scale utilization of renewable energy and distributed energy, has created a huge demand for energy storage. The gradual deepening of power market reforms also paves the way for energy storage to participate in market-oriented power grid operations. Positive factors continue to play a guiding role for the development of the energy storage industry. Over the next five years, the development of the energy storage industry remains promising. CNESA looks forward to accompanying our industry partners as we strive for the advancement of a bigger and better energy storage industry.
Author: CNESA Research Translation: George Dudley