Source: Zhuoyue Ludian
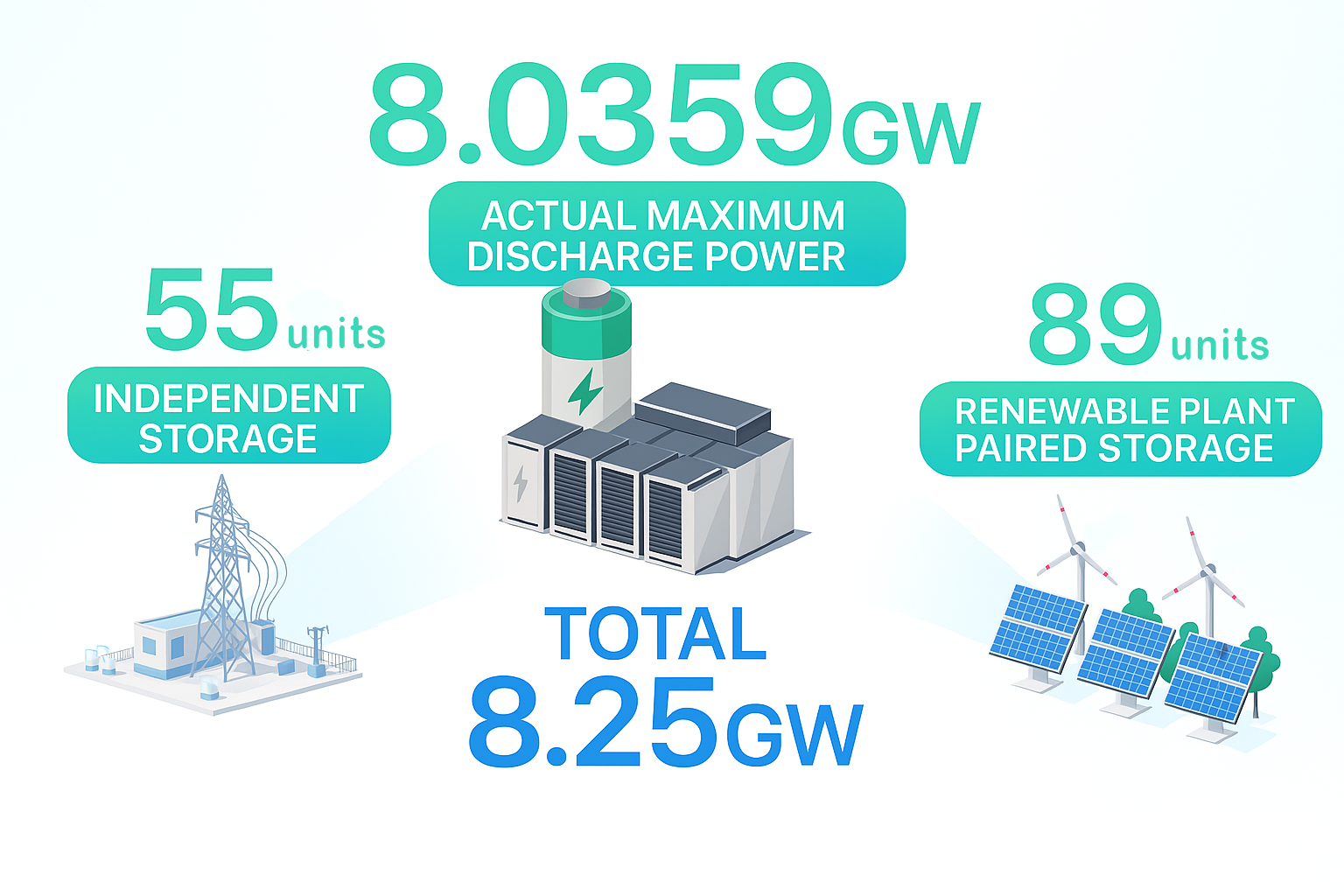
On the evening of July 11, under the unified command of the State Grid Shandong Electric Power Dispatch Center, 144 new energy storage stations in Shandong were precisely activated at the most critical moment of peak evening electricity demand, centrally delivering power to the grid. This effectively supported the evening peak of grid electricity consumption and set a new national record for a provincial-level power grid. A total of 55 independent storage units and 89 energy storage units supporting new energy power plants participated in the centralized discharge, with a total capacity of 8.25 GW and an actual maximum discharge power of 8.0359 GW.
Prior to this, Jiangsu Province had just conducted a large-scale centralized dispatch of new energy storage. On July 6, 93 new energy storage stations in Jiangsu discharged power to the grid during the evening electricity peak. A total of 64 grid-side storage stations and 29 power-source-side storage stations participated, with a total capacity of 7.248 GW and an actual maximum dispatch scale of 7.14 GW. This set a new record for centralized dispatch scale following the 4.55 GW dispatch in the summer of last year, marking a year-on-year increase of 56.9%. (For details, see “93 Energy Storage Stations Participate! Jiangsu Completes China’s Largest Centralized Dispatch of New Energy Storage”)
During the critical period of ensuring power supply in the summer peak, what is the significance of Shandong's centralized dispatch of new energy storage? How does energy storage help Shandong's power grid cope with “peak load moments”?
As is widely known, the most fundamental feature of the power system is the need to maintain real-time balance between electricity generation and consumption. However, electricity load fluctuates dynamically throughout the day, exhibiting clear peaks and valleys: during peak hours, grid load rises significantly, requiring more generation; during off-peak hours, grid load is lower, requiring less generation. This imposes a burden on grid balance.
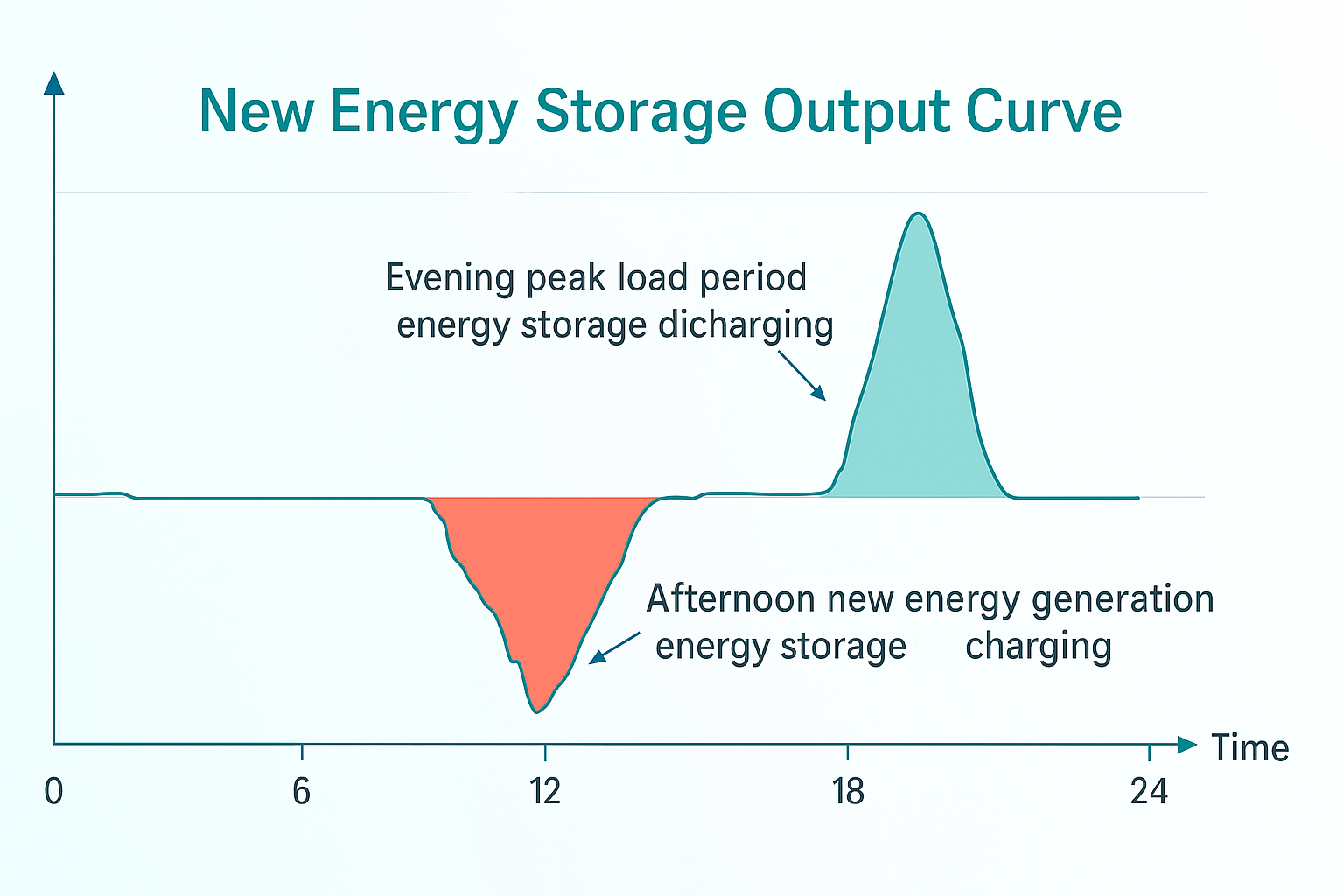
Through necessary technical and managerial means, reducing peak load and raising valley load to maintain relative balance in the power system is called peak shaving and valley filling. Energy storage facilities, which can either absorb power as a load or discharge power as a source, have thus become an important tool for peak shaving and valley filling.
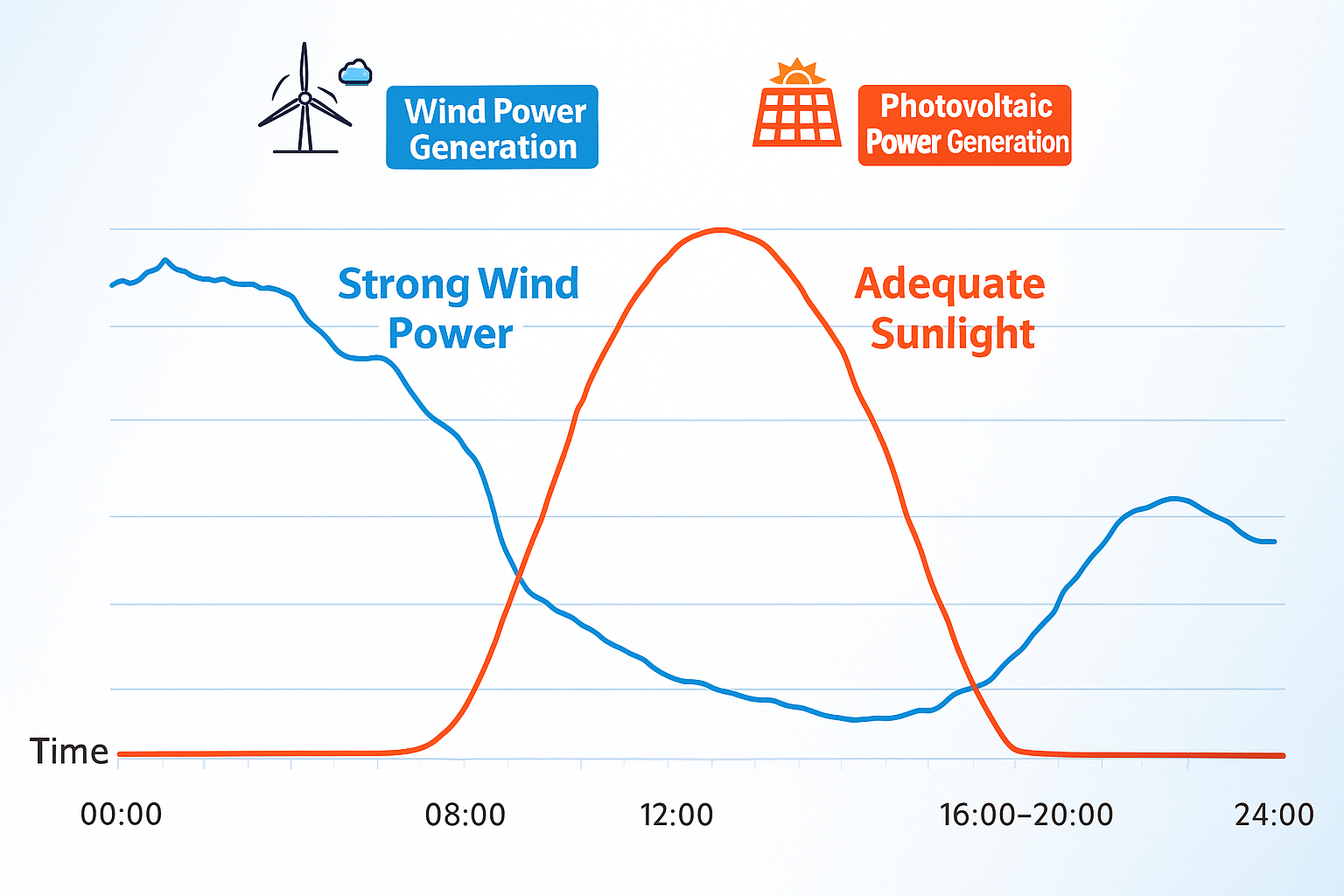
In recent years, China's rapid development of new energy has intensified the difficulty of maintaining grid balance due to its inherent randomness, intermittency, and volatility.
Take July 5 in Shandong as an example: at noon, new energy output reached a historic high of 66.615 GW, with photovoltaic output at 55.898 GW. However, during the evening peak period, photovoltaic output was nearly zero. Such significant fluctuations in output within a single day pose a great challenge to grid balance.
To mitigate the fluctuations in new energy output, energy storage systems act as “spatiotemporal regulators,” storing green electricity by “charging” during periods of abundant wind and solar power and “discharging” during peak electricity demand to support the grid. This robustly supports the province's power supply and promotes the consumption of new energy.
Based on this, as a major province in wind and solar installed capacity, Shandong has in recent years achieved “mutual advancement” in the development of new energy storage and new energy. As of now, the installed capacity of new energy storage has reached 9.4 GW, ranking third in the country, covering various forms such as electrochemical storage and compressed air storage.
In recent days, due to persistent high temperature and humidity, air conditioning and cooling load has surged, and the Shandong power grid load has broken historical records four times in a row. To effectively address the challenge of summer peak load and fully leverage the comprehensive role of new energy storage in ensuring safety, supply, and green energy consumption, State Grid Shandong Electric Power organized this centralized dispatch of new energy storage.
“This large-scale centralized dispatch of new energy storage not only reflects the overall development achievements of energy storage in Shandong, but also demonstrates the progress in constructing a new-type power system. It highlights the crucial support role of energy storage resources at critical moments. In the future, we will make greater efforts to support the development of energy storage in Shandong, further enhance grid regulation capacity, improve clean energy consumption levels, and strengthen power supply security,” said Liu Yuanlong, Director of the State Grid Shandong Electric Power Dispatch Center.
To realize the large-scale centralized dispatch of energy storage resources, in addition to a sound energy storage layout, precise and efficient dispatching methods are also indispensable.
To ensure safe and stable operation of the large power grid, the State Grid Shandong Electric Power Dispatch Center comprehensively forecasts load demand and output from various power sources such as wind, solar, and thermal. Relying on the dispatch control system, it automatically optimizes and calculates the best charge/discharge time and power for each energy storage station. During this centralized dispatch, the Dispatch Center issued charging commands to over 8.25 GW of new energy storage during peak new energy generation periods, and discharging commands during peak electricity consumption periods. Through this charge-discharge cycle, the support capacity for Shandong’s power supply has been greatly strengthened.
“In this dispatch, we took into account both societal electricity demand and grid operation safety. A total of 55 independent storage units and 89 energy storage units supporting new energy plants participated in centralized discharge, with a total capacity of 8.25 GW and an actual maximum discharge power of 8.0359 GW — equivalent to the entire grid load of Jining City,” said Zhang Bing, Director of the Dispatch Planning Division at the State Grid Shandong Electric Power Dispatch Center.
This centralized dispatch of new energy storage in Shandong demonstrates the role of energy storage in ensuring power supply at peak demand and providing emergency support. The diversification and scale of participating entities also signify that new energy storage, as a critical regulation resource, has entered a new stage in its application within new-type power systems, offering a valuable “Shandong experience” and demonstration effect for building a new energy system and safeguarding energy security.