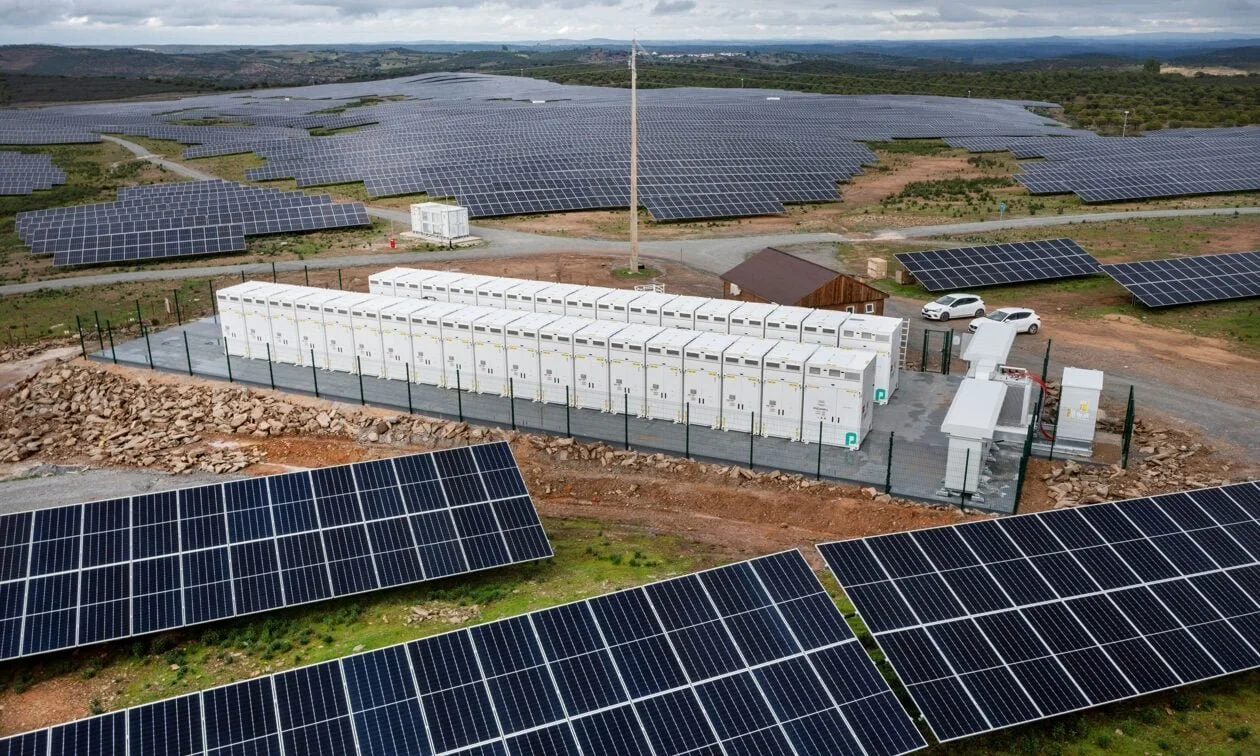
As the global energy mix accelerates its transition toward renewable energy, energy storage systems—key to balancing grid fluctuations and enhancing the consumption of green electricity—are facing increasingly urgent demands for cost reduction and efficiency improvement. In this context, increasing cell capacity has become a key focus of industry competition. From 280Ah and 314Ah to the emergence of 500Ah+ and even 600Ah+ products, the cell iteration cycle has significantly shortened. However, while large-capacity cells can reduce system costs, they also face a series of technical challenges and must undergo rigorous verification by investors regarding their safety and economic performance over the entire lifecycle. This article will analyze the internal logic and future outlook of large-capacity cell development from multiple dimensions, including technology, market, and manufacturing processes.
01 Large-Capacity Cell Deployment
As the need to reduce costs and improve efficiency in energy storage becomes increasingly urgent, cells are developing toward higher capacities. Currently, nearly 20 cell manufacturers have launched or planned 500Ah+ large-capacity cell products, and the iteration process is accelerating.
It took about three years for energy storage cells to evolve from 280Ah to 300+Ah, while it only took two years for 300+Ah cells to reach 500+Ah and even 600+Ah.
CATL is consolidating its dominant position in large-scale energy storage stations with its 587Ah cell, aiming to enhance customer service capabilities through a "high-capacity standard"; Sungrow, as a system integrator, has defined the 684Ah cell to build differentiated competitiveness through "cell-system" co-design; CALB and Rept Battero are focusing on 392Ah cell specifications to seek rapid market entry.
It is an industry trend for cell and system integration companies to increase cell capacity. However, whether project investors truly endorse large-capacity cells is still too early to determine and requires continuous market validation to assess the actual strength of large-capacity cells.
02 Why Develop Large-Capacity Cells
Cells are the most valuable component of the entire energy storage system and the main “battlefield” for ongoing iteration in storage integration technology, directly determining system configuration and integration solutions.
The fundamental purpose of building large-capacity cells is to reduce the number of cells, components, and footprint used in energy storage systems by increasing cell capacity, thereby lowering the overall investment cost of energy storage stations.
For example, CATL’s 587Ah cell can reduce the number of system components by 20% and increase space utilization by 30%. With fewer cells, the costs of connectors, fuses, BMS harnesses, and other auxiliary materials are significantly reduced.
From a system O&M cost perspective, for energy storage systems with the same capacity, the significantly reduced number of large-capacity cells means fewer potential failure points, lower monitoring and maintenance complexity, and reduced lifecycle O&M costs.
03 Technical Challenges of Large-Capacity Cells
During cell charging and discharging, when capacity exceeds 500Ah, electrode thickness must increase from 150μm to 250μm. The diffusion distance of Li⁺ in the LiFePO₄ lattice becomes longer, impeding internal electrochemical reactions and causing increased polarization voltage near the end of charging, which accelerates cell aging and shortens lifespan. Furthermore, increased polarization voltage at the end of charging generates excessive internal heat, potentially leading to thermal runaway, causing fires, explosions, and other safety incidents.
In manufacturing, electrode sheets require extremely high coating uniformity. As electrode size increases, thickness deviation also increases. The welding area of tabs in large-capacity cells is larger, increasing the probability of false welding or burn-through. During formation, uneven current distribution may cause inconsistent SEI film formation, affecting lifecycle consistency.
In system integration, large-capacity cells pose challenges in refined management and risk control. In a large-capacity system, the importance of a single cell increases significantly. In a 314Ah system, a single cell failure affects about 0.3% of cluster capacity, while in a 684Ah system, a single cell failure may affect 0.6% of cluster capacity. The long heat dissipation paths and high thermal resistance in large cells hinder quick heat transfer, demanding high reliability in thermal management design. To improve cooling, higher flow and pressure liquid cooling pumps are needed to ensure rapid circulation of coolant, and the related thermal components must offer superior heat dissipation performance and reliability.
At the application level, 314Ah systems are already mature. For investors, the safety, lifespan, and stability of large-capacity cell integration solutions are still based only on supplier reports without reliable operational data. The actual performance of large cells in operation remains uncertain, and in the short term, accepting large-cell integration solutions may face considerable challenges.
Therefore, the large-scale application of large-capacity cells will not happen overnight. Cell manufacturers will weigh process difficulty, cost, and market acceptance, while investors will consider safety, economic benefits, and convenience of cell replacement.
04 Manufacturing Process
Due to differences in R&D direction and technical accumulation among companies, there are divergent approaches to manufacturing large-capacity cells. The main manufacturing processes for 500Ah+ cells are winding and stacking.
Advantages of the stacking process: Stacked electrode groups are layered structures without bending, making full use of case space. Compared to winding, stacking offers higher energy density, lower internal resistance, lower temperature rise, better rate performance, and improved safety.
Disadvantages of the stacking process: Electrodes must be cut before stacking, and the cut surfaces may have burrs and dust, creating risk of internal short circuits. High precision is required in burr and alignment control during processing. High-precision semi- or fully-automated equipment is needed for trimming control, resulting in higher equipment and production costs.
Advantages of the winding process: The roll core is formed through high-speed rotation with minimal mechanical action and short auxiliary time, yielding high production efficiency. Winding requires only two spot welds per cell and is relatively simple to operate. Winding machines are cheaper, with lower investment cost.
Disadvantages of the winding process: With single tabs on positive and negative electrodes, part of the voltage is lost in internal polarization, resulting in poor charge/discharge rate performance. During winding, uneven tension on electrodes and separators can cause wrinkles. Electrode expansion and contraction impact cell cycle life.
05 Standardization or Diversification
After the issuance of Document No. 136, the marketization of energy storage station investment and operation accelerated. Investors are focusing more on the full-lifecycle revenue of storage equipment. Since the industry has reached consensus on “thermal runaway warning thresholds” and “cycle life bottom lines” for cells, a safety baseline has been established for system adaptation across different cell sizes. Additionally, on the communication layer, BMS-cell communication protocols and state monitoring parameters are gradually being unified, enabling different cell sizes to connect to the same monitoring system. Against this backdrop, the evolution of storage cell size is not a binary choice but a dynamic process of maintaining differentiated innovation within a unified framework.
Therefore, in the short term, differences in priority regarding capacity, density, cost, and safety across various markets drive divergent design logic. A competitive structure will emerge with 314Ah, 392Ah, and 500Ah+ cells complementing each other. The 314Ah and 392Ah cells will continue to dominate the 2h and 4h storage markets, while 500Ah+ will focus on long-duration storage above 4h. Furthermore, as market competition intensifies, companies with different market standings are adopting divergent strategies to capture market share. Leading enterprises promote single-standard products to redefine the next generation of cell size; second- and third-tier companies pursue multi-specification strategies to meet diverse customer needs, resulting in short-term intensification of cell size diversification and a blooming landscape.
In the long term, as storage duration increases and large-cell manufacturing advances, whether it’s 530Ah, 587Ah, or 684Ah cells, their application performance across various markets and their impact on station and system design will be critical. Integrators will choose appropriate technical paths based on these factors, further reinforcing size diversity. The winding process, with its lower overall manufacturing cost, will target the sub-600Ah market, while stacking—offering uniform internal stress distribution and low heat generation—will aim at the 600Ah+ segment.
06 Trend Outlook
Cells should not simply pursue larger capacity but also consider investor acceptance. Therefore, large-cell development should start from aspects such as energy storage systems, AC-side distribution, and post-operation and maintenance, exploring technical innovation paths to reduce LCOS costs.
Although 500Ah+, 700Ah+, and even 1000Ah+ cells are emerging one after another, large-capacity cells have yet to achieve large-scale deployment. It is still too early to determine which type will become the mainstream next-generation product. Ultimately, the winning cell type will depend on a company’s deep understanding of system boundaries, rational judgment of technical tipping points, and flexible responsiveness to application scenario demands.