During the 14th Five-Year Plan period, China’s energy storage technology mix witnessed noticeable changes where pumped hydro storage accounted for less than 40% for the first time while the new-type energy storage represented by lithium batteries saw explosive growth.
According to incomplete statistic from China Energy Storage Alliance (CNESA), by the end of 2025, China’s cumulative installed capacity of power storage reached 213.3GW among which pumped hydro storage shared 31.3% while the new-type cumulative energy installations represented by lithium battery accounted for over two thirds.
Against the backdrop of robust industry expansion, it is significant to improve energy storage standardization system especially enhancing safety standard.
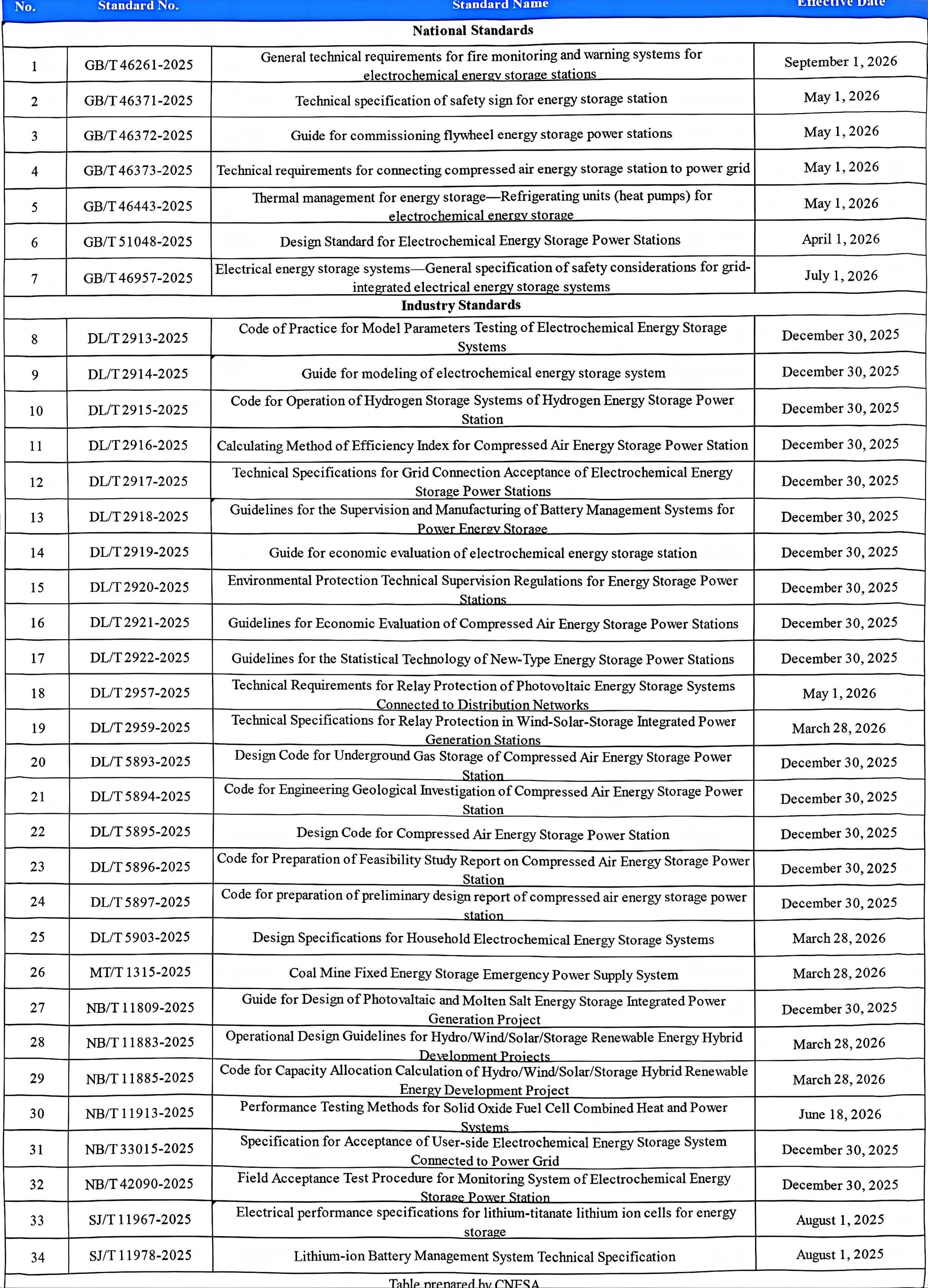
Through the incomplete statistic, in 2025, China released over 40 national, industry and local standards on energy storage. These standards cover energy storage planning and designing, equipment testing, grid connection and operation, safety management and emergency response, providing important support to guide high-quality industry development, guarantee the safety of energy storage power stations, and promote the energy structure transformation and the green and low-carbon development across industrial value chain.
This article aims to clarify major energy storage standards released in 2025 and their influence. It will also list the key standards that have already come into force or will be implemented in 2026, helping industry stakeholder stay aligned with regulatory developments, mitigate compliance risks, and ensure the safe and efficient advancement of projects.
Strengthening the Energy Storage Safety Standards System From “Recommended” to “Mandatory”
Electrochemical Energy Storage represented by lithium battery has developed in a breakneck speed where installed capacity continued to expand, with safety being a core concern for the industry. In accordance with the incomplete statistic, 2025 alone saw about 30 energy storage safety accidents across the world. Two fires happened consecutively in American Moss Landing energy storage plant with huge loss, drawing widespread attention.
In order to ensure the safe and stable operation of lithium battery energy storage systems, cut down accident incidences and improve emergency response capabilities, the mandatory national standard GB 44240 Secondary lithium cells and batteries used in electrical energy storage systems—Safety requirements officially came into effect on August 1, 2025, which is recognized as the highest-level national standard on energy storage safety to date. It upgrades the safety requirements of energy storage lithium battery from “recommended” to “mandatory” for the first time, covering more than 20 rigorous testings from cell vibration, acceleration shock, shallow puncture, and compulsory discharge. Several leading companies’ battery products like those of CATL have passed third-party testings which is a sign that the standard’s entry into substantive implementation, setting a new benchmark for energy storage industry.
China’s Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development released the revised national standard GB/T 51048- 2025 Design Standard for Electrochemical Energy Storage Power Station. Issued on December 31, 2025 and effective on April 1, 2026, this standard represents the first revision in a decade. Through revision across ten years, it introduces new technology pathways of sodium batteries, hydrogen fuel cells and so on. Based on practical challenges encountered during the application of electrochemical energy storage pathways over the past ten years, it established differentiated design requirements and addressing the potential safety risks serves as a core technical reference for the design of electrochemical energy storage power stations.
Shifting the Focus of Safety Protection from “Post-Incident Response” to “Pre-Incident Prevention”
With the continuous breakthroughs of safety protection technologies, shifting from “post-incident response” to “pre-incidence prevention” gradually become one of the major strategies.
China’s first national electrochemical energy storage fire warning standard GB/T 46261- 2025 General technical requirements for fire monitoring and warning systems for electrochemical energy storage stations was issued on August 29, 2025 and will take effect on September 1, 2026. This standard established a systematic and standardized framework for fire monitoring and early warning systems for the first time, covering several performances and technology requirements like multi-parameter monitoring, coordinated control and environmental adaptability and filling the long-standing gap in standards for early fire monitoring and warning product, which holds important reference for accident monitoring and safety warning system design in energy storage power stations.
CNESA standard Technical Specification for Liquid Nitrogen Fire Extinguishing Systems in Electrochemical Energy Storage Power Stations is currently under public consultation. Developed based on national key R&D program outcomes, the standard consolidates technical achievements in liquid nitrogen fire suppression systems and their application in protecting lithium-ion battery energy storage systems.
Internationally, the 2026 edition of NFPA 855 has also placed pre-incident prevention at the center of safety management. Systematic risk identification and mitigation analysis have been upgraded from conditional to routine requirements. It firstly introduced large-scale fire testings on the assessment of thermal runaway propagation. CSA/ANSI C800-2025 and the fifth edition of UL 9540A came as follows, which update large-scale fire testings requirements and significantly improve the proactive safety protection requirements of energy storage products.
Initial Progress Energy Storage Footprint Accounting Standards Supporting the “Dual Carbon” Goals
As the GB/T 24067- 2024 Greenhouse gases—Quantification methods and requirements for carbon footprint of product—Lithium-ion battery for electrical energy storage systems releases, China has built the foundational framework of carbon footprint accounting. Subsequently, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment together with National Development and Reform Commission and other authorities jointly issued the Guidelines for Developing Product Carbon Footprint Accounting Standards, encouraging broad participation in the design and amendment of product carbon footprint accounting standards. The guidelines target the formulation of 100 product carbon footprint standards by 2027 and 200 by 2030. Building on this framework, sector-specific carbon footprint standards are now gradually being developed.
In 2025, draft standards such as Greenhouse Gases—Product Carbon Footprint Quantification Requirements for Lithium-Ion Batteries Used in Electrical Energy Storage Systems, led by the China Electronics Standardization Institute, and Greenhouse Gases—Product Carbon Footprint Quantification Methods and Requirements for Lithium Battery Energy Storage Systems, jointly led by Shanghai Envision KES Technology Co., Ltd. and CNESA, entered the public consultation phase. Once released, these standards will provide clear and consistent methodologies for carbon footprint accounting for lithium-ion batteries and energy storage systems.
Conclusion
2025 marked an important year in the standardization of China’s energy storage sector with a set of critical safety standards releasing and implementing, providing essential guidance for the safe development of the industry. As energy storage technologies continue to develop and innovate, sustained collaboration among stakeholders and active participation in standardization efforts will remain critical to fostering a healthy energy ecosystem, supporting China;s energy transition, and advancing green and low-carbon development.
Appendix: Key Energy Storage Standards for 2026
Register now to attend Asia’s Largest Energy Storage Trade Show for free:
What: The 14th Energy Storage International Conference & Expo
When: Conferences: March 31 - April 2, 2026
Exhibitions: April 1-3, 2026
Where: CIECC Beijing, China
Address: No. 55 Yudong road, Shunyi District, Beijing China